Vector Spaces
Approximate Match
Annoy (Approximate Nearest Neighbor Oh Yeah)
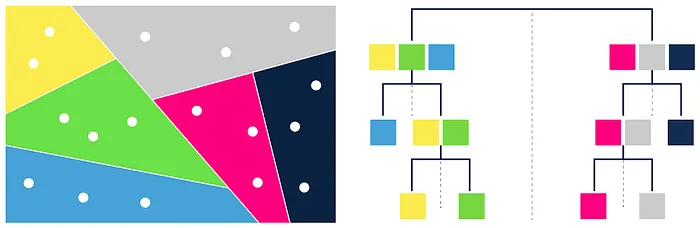
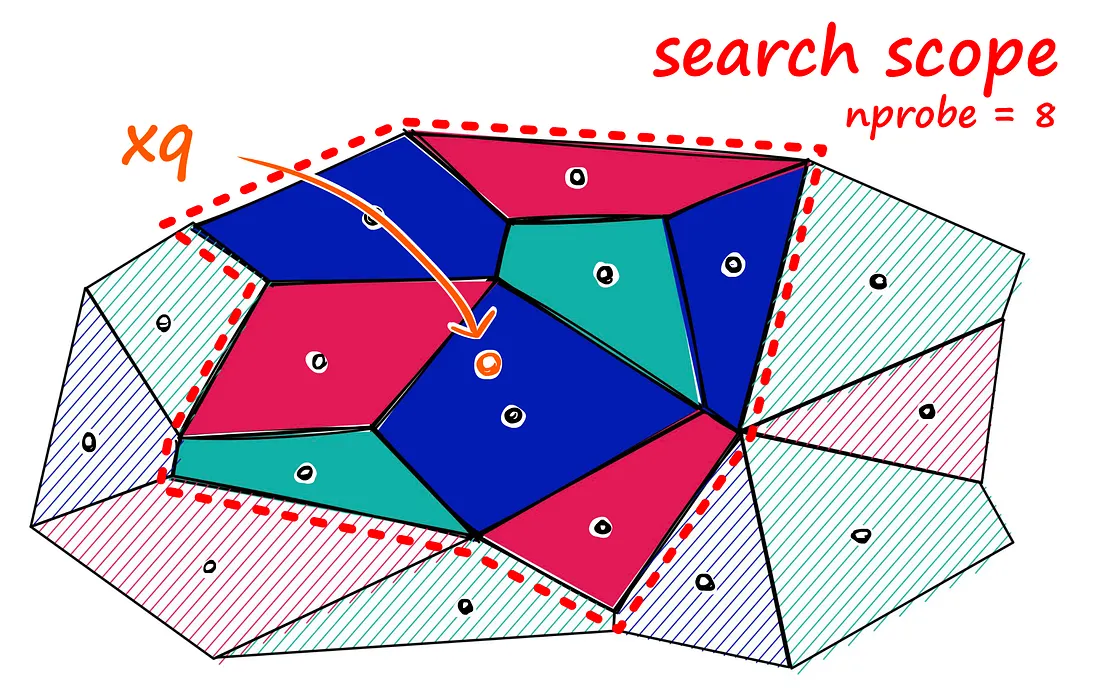
Inverted File (IVF) Indexing
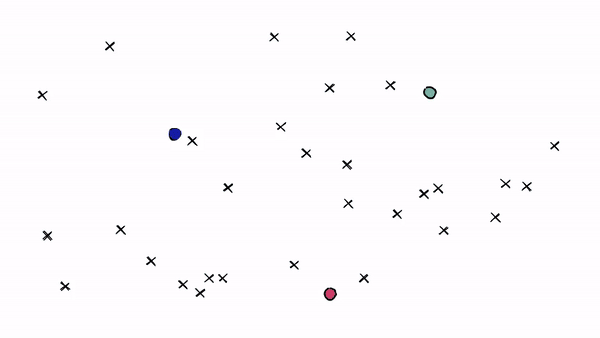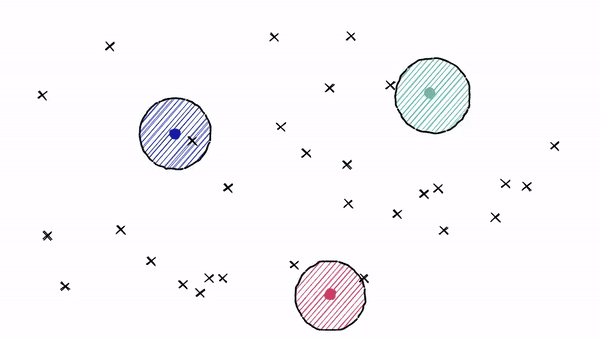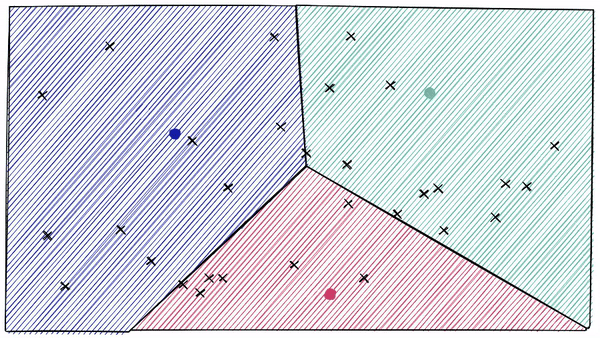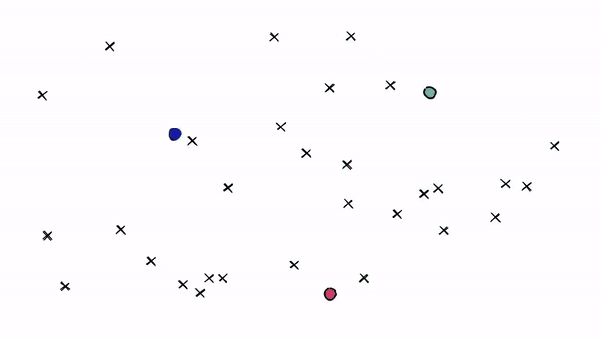
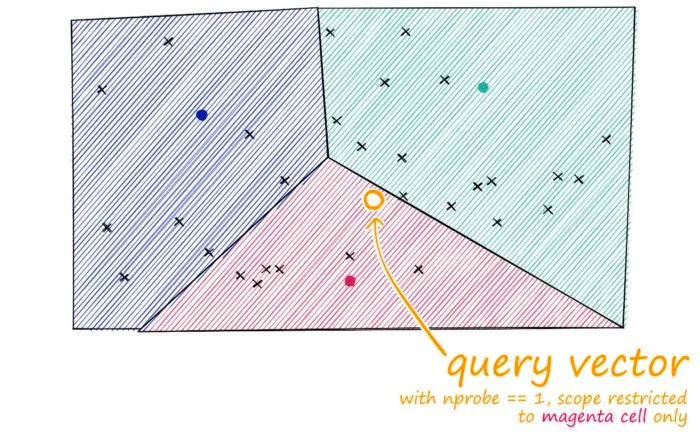
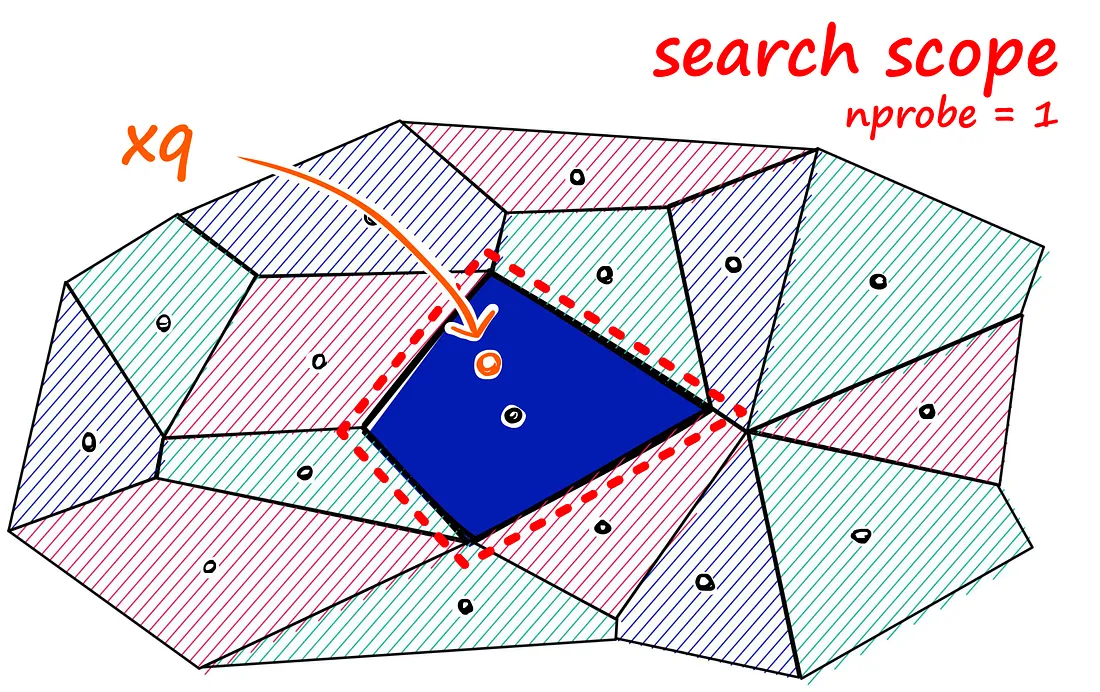
But there is a problem if our query vector lands near the edge of a cell — there’s a good chance that its closest other datapoint is contained within a neighboring cell. We call this the ==edge problem====:
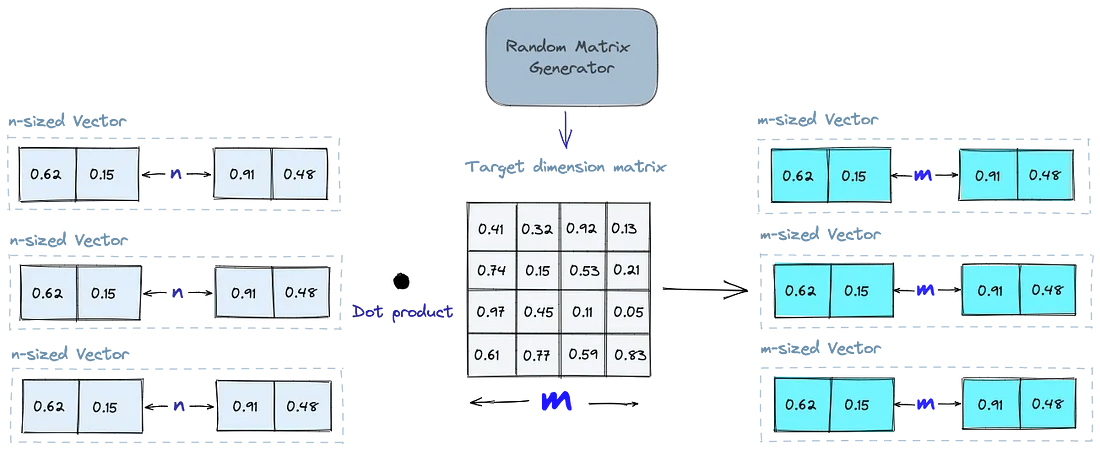
Random Projection (RP)
The basic idea behind random projection is to project the high-dimensional vectors to a lower-dimensional space using a random projection matrix. When we query, we use the same projection matrix to project the query vector onto the lower-dimensional space. Then, we compare the projected query vector to the projected vectors in the database to find the nearest neighbors.
Product Quantization (PQ)
- Splitting -The vectors are broken into segments.
- Training — we build a “codebook” for each segment. Simply put — the algorithm generates a pool of potential “codes” that could be assigned to a vector. In practice — this “codebook” is made up of the center points of clusters created by performing k-means clustering on each of the vector’s segments. We would have the same number of values in the segment codebook as the value we use for the k-means clustering.
- Encoding — The algorithm assigns a specific code to each segment. In practice, we find the nearest value in the codebook to each vector segment after the training is complete. Our PQ code for the segment will be the identifier for the corresponding value in the codebook. We could use as many PQ codes as we’d like, meaning we can pick multiple values from the codebook to represent each segment.
- Querying — When we query, the algorithm breaks down the vectors into sub-vectors and quantizes them using the same codebook. Then, it uses the indexed codes to find the nearest vectors to the query vector.

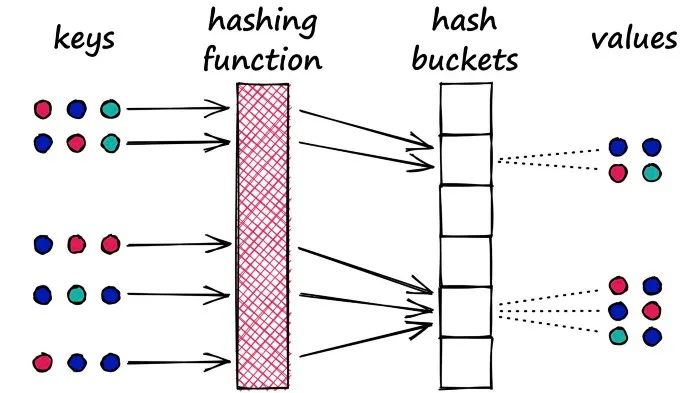
Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH)
for LSH, we want to maximize hashing collisions.
Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW)
HNSW creates a hierarchical, tree-like structure where each node of the tree represents a set of vectors. The edges between the nodes represent the ==similarity between the vectors.==
Bunu çok anlamadım. Kullanılacaksa daha detaylı araştıracağım.
Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN)
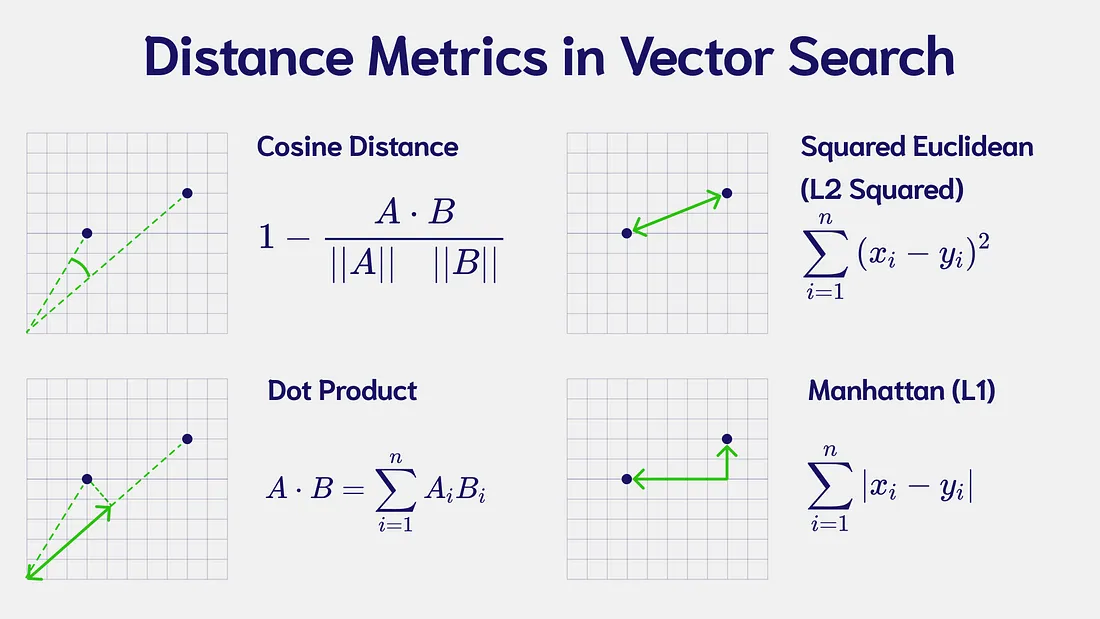
Similarity Measures: Distance Metrics
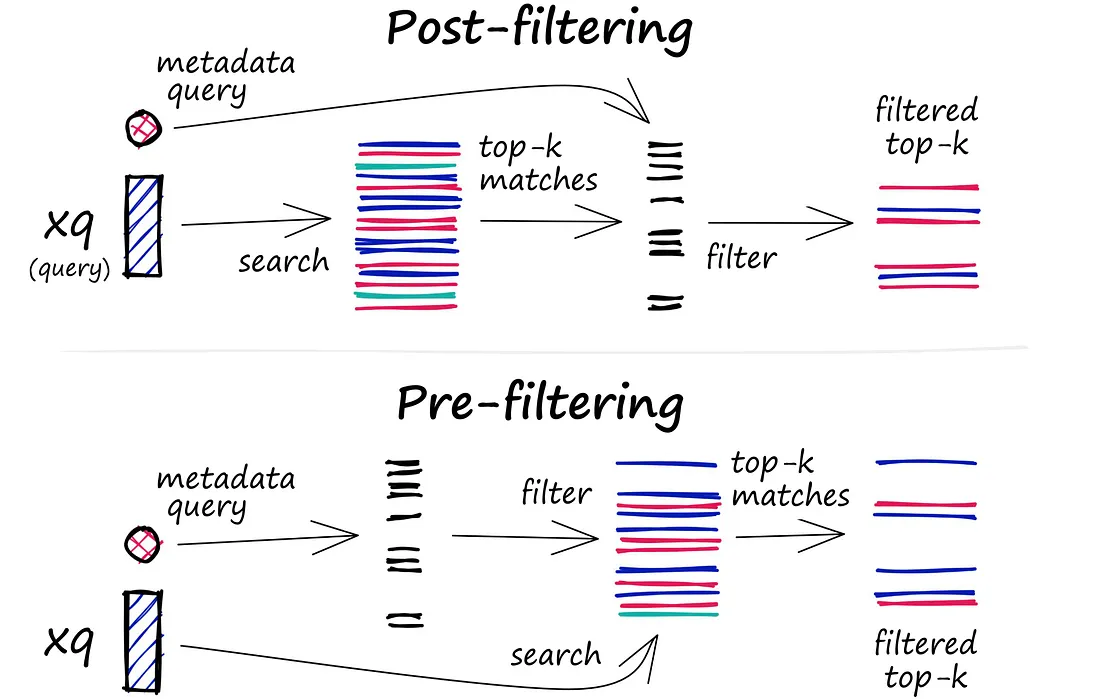
Filtering
Every vector stored in the database also includes metadata. In addition to the ability to query for similar vectors, vector databases can also filter the results based on a metadata query.
Filtering dediğimiz şey metadata’ya göre filterlama oluyor
It then performs the metadata filtering either before or after the vector search itself,